Categories
- Bariatric Surgery (11)
- Black Fungus (5)
- Bone Marrow transplant (3)
- Brain Tumor Surgery Navigation Technology (20)
- Cardiac Surgery (66)
- Cardiology (97)
- Computer navigation technology for joint replacements (20)
- Covid Vaccination (17)
- Critical Care (2)
- Dental (19)
- Dermatology (31)
- Dialysis Support Group - “UTSAAH” (11)
- Dietitian (33)
- Emergency Medicine (4)
- Emotional Health (11)
- Endocrinology (33)
- ENT (20)
- Gastroenterology and GI Surgery (53)
- General and Laparoscopic Surgery (21)
- General Surgery (4)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (183)
- Hematology (20)
- Internal Medicine (294)
- Kidney Transplant (50)
- Kidney Transplantation (20)
- Lung Cancer (8)
- Minimal Invasive Surgery (1)
- Mother & Child (20)
- mucormycosis (5)
- Nephrology (61)
- Neurology (147)
- Neurosurgery (68)
- Nutrition and Dietetics (107)
- Omicron Variant (1)
- Oncology (288)
- Ophthalmology (10)
- Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement (86)
- Paediatrics (59)
- Pediatric Nephrology (3)
- Physiotherapy (5)
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery (6)
- Psychiatry and Psychology (90)
- Psychologist (28)
- Pulmonology (72)
- Rheumatology (13)
- Spine Services (21)
- Transradial Angioplasty (16)
- Urology (84)
Query Form
Posted on Apr 19, 2022
Effect of diabetes on the kidneys?
Diabetes affects the kidneys, causing diabetic kidney disease. It also affects the gastrointestinal tract, causing complications such as intestinal enteropathy, gastroparesis, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes also causes your gums and teeth to inflame, thus leading to the destruction of the teeth, bone, gums, and fibers that support the gums.
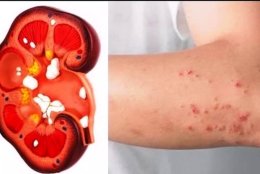
SYMPTOMS OF KIDNEY DISEASE:
At the initial stages, the disease may be asymptomatic the only sign of diabetic kidney disease is high protein levels in urine. Some of the symptoms, which develop later, may include:
- Fluid retention
- Nausea and vomiting
- Muscle cramps
- Puffiness around the eyes
- Dry and itchy skin
- Weight loss
DIAGNOSIS ASSOCIATED WITH KIDNEY DISEASE:
Diabetic nephropathy is diagnosed by using the following tests:
- Microalbuminuria in urine.
- Serum creatinine level
- Kidney Biopsy
- BUN blood test:
TREATMENT KIDNEY DISEASE DUE TO DIABETES:
- Prevention: It includes good control of blood glucose levels and blood pressure.
- Medication: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers are used to reduce the high blood pressure.
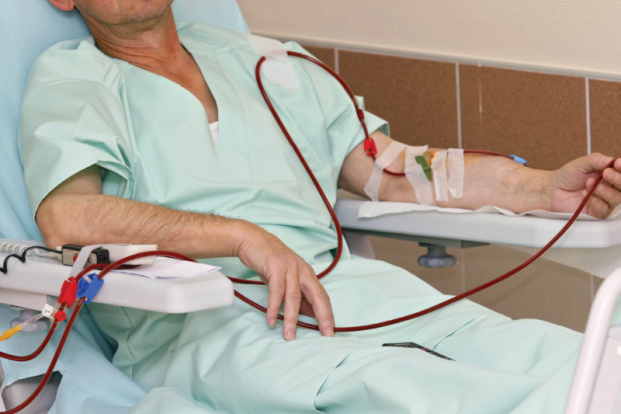
- Dialysis: It is a supportive treatment when the kidneys stop functioning normally. It involves either shunting the patient’s blood through a special machine that helps to remove the wastes by preserving water and salts or removing the wastes through fluid introduced into the abdomen.
- Kidney transplant: A healthy donor kidney is obtained either from someone who has died or from a relative or friend (from a compatible donor) to replace the diseased kidney.
PREVENTIVE MEASURES TO REDUCE THE RISKS
- Controlling the blood sugar levels
- Avoiding the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Treating the urinary tract infections
- Drinking plenty of non-alcoholic fluids
- Avoiding medical treatments that stress the kidneys
- Avoiding the use of tobacco products
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining healthy weight
- Eating healthy foods