Categories
- Bariatric Surgery (11)
- Black Fungus (5)
- Bone Marrow transplant (3)
- Brain Tumor Surgery Navigation Technology (20)
- Cardiac Surgery (66)
- Cardiology (97)
- Computer navigation technology for joint replacements (20)
- Covid Vaccination (17)
- Critical Care (2)
- Dental (19)
- Dermatology (31)
- Dialysis Support Group - “UTSAAH” (11)
- Dietitian (33)
- Emergency Medicine (4)
- Emotional Health (11)
- Endocrinology (33)
- ENT (20)
- Gastroenterology and GI Surgery (53)
- General and Laparoscopic Surgery (21)
- General Surgery (4)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (183)
- Hematology (20)
- Internal Medicine (294)
- Kidney Transplant (50)
- Kidney Transplantation (20)
- Lung Cancer (8)
- Minimal Invasive Surgery (1)
- Mother & Child (20)
- mucormycosis (5)
- Nephrology (61)
- Neurology (147)
- Neurosurgery (68)
- Nutrition and Dietetics (107)
- Omicron Variant (1)
- Oncology (288)
- Ophthalmology (10)
- Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement (86)
- Paediatrics (59)
- Pediatric Nephrology (3)
- Physiotherapy (5)
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery (6)
- Psychiatry and Psychology (90)
- Psychologist (28)
- Pulmonology (72)
- Rheumatology (13)
- Spine Services (21)
- Transradial Angioplasty (16)
- Urology (84)
Query Form
Posted on Apr 19, 2022
Is Malaria a virus?
Malaria is a mosquito-borne parasitic infection which is transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes. The Plasmodium parasite that causes malaria is neither a virus nor bacteria. It is a single cell parasite which multiplies in the RBC of human and mosquito intestine.
The incubation period of the disease depends according to the species of Plasmodium. When the female mosquito feeds on the infected person, Parents parasites are ingested into the mosquito’s gut along with human Board.
The four species of Plasmodium that can cause malaria infection are Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malaria. Plasmodium falciparum is the most dangerous one and can cause death.
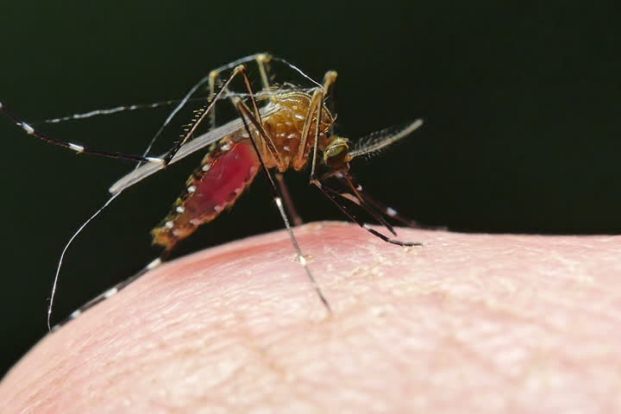
Malaria is caused by the bite of the infected mosquito, or if the infected blood is received from someone through blood transfusion. The mosquito after biting the infected person or animal carries plasmodium parasite which then, goes various changes to infect the next person the mosquito feeds on. Plasmodium enters the bloodstream & invades the RBC & multiples in RBC. As a result, the infected RBCs burst and the parasites are disseminated into the body causing the symptoms of malaria.
People having sickle cell anemia have the immunity against malaria. The same is the case with thalassemia.
Signs and Symptoms associated with Malaria:
Symptoms usually appear in 1 to 3 weeks after infection. Some of the symptoms include are
- Chills and sweat
- Abdominal pain, Headache
- High fevers
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
- Poor Appetite
- Muscle aches
Plasmodium vivax can lie dormant in the liver for several days to months before causing any symptoms. If recognized early, the infection of malaria can be completely treated.