Categories
- Bariatric Surgery (11)
- Black Fungus (5)
- Bone Marrow transplant (3)
- Brain Tumor Surgery Navigation Technology (20)
- Cardiac Surgery (66)
- Cardiology (97)
- Computer navigation technology for joint replacements (20)
- Covid Vaccination (17)
- Critical Care (2)
- Dental (19)
- Dermatology (31)
- Dialysis Support Group - “UTSAAH” (11)
- Dietitian (33)
- Emergency Medicine (4)
- Emotional Health (11)
- Endocrinology (33)
- ENT (20)
- Gastroenterology and GI Surgery (53)
- General and Laparoscopic Surgery (21)
- General Surgery (4)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (183)
- Hematology (20)
- Internal Medicine (294)
- Kidney Transplant (50)
- Kidney Transplantation (20)
- Lung Cancer (8)
- Minimal Invasive Surgery (1)
- Mother & Child (20)
- mucormycosis (5)
- Nephrology (61)
- Neurology (147)
- Neurosurgery (68)
- Nutrition and Dietetics (107)
- Omicron Variant (1)
- Oncology (288)
- Ophthalmology (10)
- Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement (86)
- Paediatrics (59)
- Pediatric Nephrology (3)
- Physiotherapy (5)
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery (6)
- Psychiatry and Psychology (90)
- Psychologist (28)
- Pulmonology (72)
- Rheumatology (13)
- Spine Services (21)
- Transradial Angioplasty (16)
- Urology (84)
Query Form
Posted on Apr 19, 2022
Lower Back Pain: Causes and Diagnosis
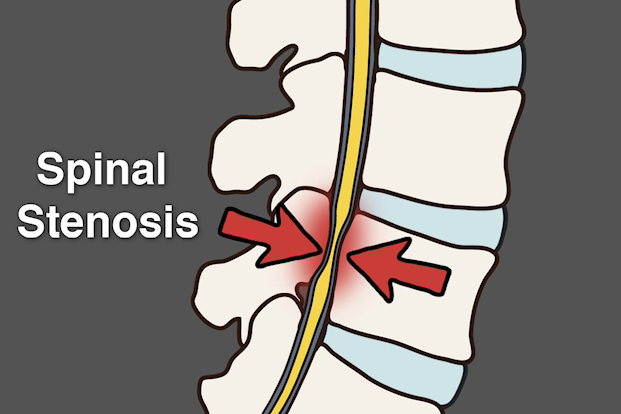
Lower Back Pain (LBP) refers to pain in the back arising between the D12 vertebra and pelvis. This is caused due a variety of reasons – protruded lumbar intervertebral disc (PIVD), lumbar canal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, deformity, infection (tuberculosis or pyogenic), post traumatic – fracture / spondylolysis, tumor or metastasis of lumbar vertebrae, osteoporotic fracture.
Non specific LBP is said to occur if LBP exists in absence of above causes and occurs due to bad postures, unhealthy habits, prolong sitting, psychological / compensation related issues. Systemic diseases – renal disease, pancreatitis and uterine fibroid, abdominal tumors can also have associated LBP.
What kind of lower back pain needs immediate attention?
LBP with severe acute onset pain, weakness/ pain in legs, loss of control over urination / defecation, weight loss, trauma, pain while in bed, pain affecting activities of daily living, past history with tumor needs to be investigated on priority basis. If not so, LBP can be treated with medication, physiotherapy, lifestyle improvement.
How does the doctor diagnose and treat lower back pain?
90% of diagnosis can be made by good history and clinical examination. Clinician notes- type of pain, duration, aggravating and reliving factors, how it is affecting lifestyle and so on. During examination clinician checks gait of person, neurological status, difficulty in performing routine activities. This is further substantiated with help of various investigations.
Primary investigation includes – X rays- this demarcates bony outline, bony destruction, soft tissue shadow- abscess, loss of disc height, any fracture, deformity or progression of deformity. X rays done in dynamic views helps to diagnose instability.
- MRI – MRI is more specific and sensitive. It helps in diagnosis of lumbar protruded intervertebral disc, lumbar canal stenosis, tumor, infection- tuberculosis of spine and other pathology. Mri also diagnoses skip lesion affecting other vertebrae. It helps to quantify the compression over spinal cord and nerves, presence of spinal cord edema and myelopathy. This also helps in diagnosis of pathology affecting junction areas.
- CT scan – similar to MRI, CT scan is specific. It gives more information about bony structure than soft tissues.
- Bone Scan /PET CT – helps in diagnosis of metastasis.
- Blood investigations– TLC, Hemoglobin, ESR, CRP etc helps in confirming diagnosis.
Thorough history and clinical examination along with radiological and blood investigations helps in diagnosis of LBP.