Categories
- Bariatric Surgery (11)
- Black Fungus (5)
- Bone Marrow transplant (3)
- Brain Tumor Surgery Navigation Technology (20)
- Cardiac Surgery (66)
- Cardiology (97)
- Computer navigation technology for joint replacements (20)
- Covid Vaccination (17)
- Critical Care (2)
- Dental (19)
- Dermatology (31)
- Dialysis Support Group - “UTSAAH” (11)
- Dietitian (33)
- Emergency Medicine (4)
- Emotional Health (11)
- Endocrinology (33)
- ENT (20)
- Gastroenterology and GI Surgery (53)
- General and Laparoscopic Surgery (21)
- General Surgery (4)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (183)
- Hematology (20)
- Internal Medicine (294)
- Kidney Transplant (50)
- Kidney Transplantation (20)
- Lung Cancer (8)
- Minimal Invasive Surgery (1)
- Mother & Child (20)
- mucormycosis (5)
- Nephrology (61)
- Neurology (147)
- Neurosurgery (68)
- Nutrition and Dietetics (107)
- Omicron Variant (1)
- Oncology (288)
- Ophthalmology (10)
- Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement (86)
- Paediatrics (59)
- Pediatric Nephrology (3)
- Physiotherapy (5)
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery (6)
- Psychiatry and Psychology (90)
- Psychologist (28)
- Pulmonology (72)
- Rheumatology (13)
- Spine Services (21)
- Transradial Angioplasty (16)
- Urology (84)
Query Form
Posted on Apr 19, 2022
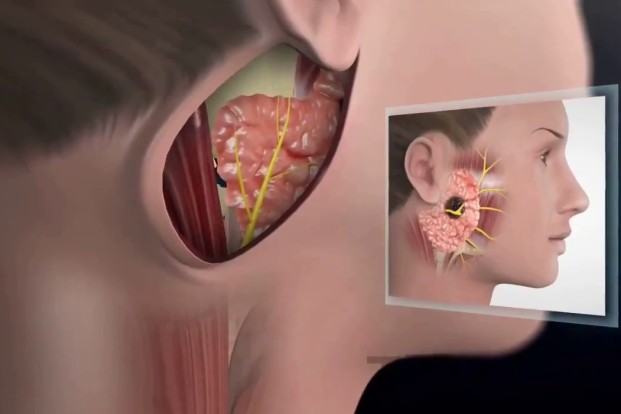
Parotid Tumours
Parotid tumours are most common tumours of all salivary gland tumours and account for about 85% of all salivary gland tumours.
Most of parotid gland tumours are benign. Less than 20% are malignant in nature.
Parotid gland is located in front of the ear in cheek area and produce saliva. They are the largest salivary glands.
Most common presentation is swelling below and in front of the ear lobule. Rarely in cases of advanced cancer, patient may present with symptoms pertaining to facial nerve involvement , pain etc.
Diagnosis is made primarily by clinical examination followed by ultrasound and MRI along with FNAC to know the exact nature and extent of disease.
Most common variety is pleomorphic adenoma which is benign but has high tendency of local recurrence if complete removal is not done.
Treatment consists of removing either the superficial lobe or complete removal of parotid. During surgery, special care is needed to avoid injury to facial nerve and its branches. Facial nerve is an important nerve which controls the facial expressions and movement. Facial nerve and its branches passes between the two lobes of parotid gland.
The most common complication of surgery is injury to marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve which controls the angle of the mouth. In various series the reported incidence is in tune of around 50%.
The other common complication is Frey’s syndrome and salivary leak. Freys syndrome is sweating while eating food and is present in subclinical form in majority of patients.
Radiation and sometimes chemotherapy is needed in malignant tumours along with surgical excision if possible.
In case of diagnosis of parotid cancer, please consult your doctor for treatment modality.