Categories
- Bariatric Surgery (11)
- Black Fungus (5)
- Bone Marrow transplant (3)
- Brain Tumor Surgery Navigation Technology (20)
- Cardiac Surgery (66)
- Cardiology (97)
- Computer navigation technology for joint replacements (20)
- Covid Vaccination (17)
- Critical Care (2)
- Dental (19)
- Dermatology (31)
- Dialysis Support Group - “UTSAAH” (11)
- Dietitian (33)
- Emergency Medicine (4)
- Emotional Health (11)
- Endocrinology (33)
- ENT (20)
- Gastroenterology and GI Surgery (53)
- General and Laparoscopic Surgery (21)
- General Surgery (4)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (183)
- Hematology (20)
- Internal Medicine (294)
- Kidney Transplant (50)
- Kidney Transplantation (20)
- Lung Cancer (8)
- Minimal Invasive Surgery (1)
- Mother & Child (20)
- mucormycosis (5)
- Nephrology (61)
- Neurology (147)
- Neurosurgery (68)
- Nutrition and Dietetics (107)
- Omicron Variant (1)
- Oncology (288)
- Ophthalmology (10)
- Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement (86)
- Paediatrics (59)
- Pediatric Nephrology (3)
- Physiotherapy (5)
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery (6)
- Psychiatry and Psychology (90)
- Psychologist (28)
- Pulmonology (72)
- Rheumatology (13)
- Spine Services (21)
- Transradial Angioplasty (16)
- Urology (84)
Query Form
Posted on Apr 19, 2022
SIDE EFFECTS OF RADIATION THERAPY
Radiation therapy damages cancer cells and also damages the healthy cells during the treatment. Damage to healthy cells causes side effects. Side effects depend on what part of the body receives radiation therapy. Different cells and tissues in the body cope differently with radiation. The side effects of radiation therapy vary from patient to patient. The side effects are specific to the area being treated, so two patients being treated for different cancers could have very different experiences. It is important to talk about possible side effects and tips for managing them. Rapidly dividing cells are affected the most. These include skin cells, cells lining the mouth and gastrointestinal (GI) tract and blood cells in the bone marrow.
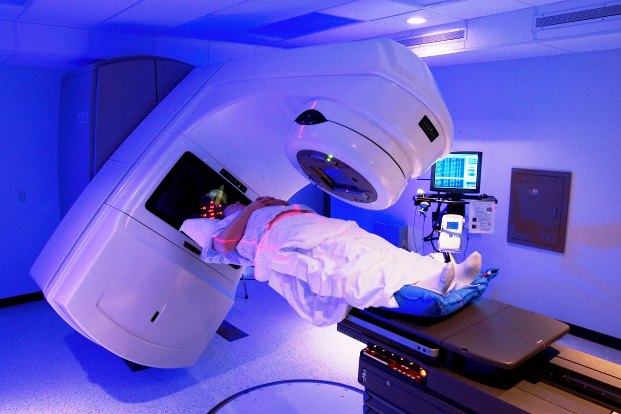
In general, the side effects of radiation therapy will depend on:
- The type of radiation therapy
- The part of body being treated
- The amount (dose) of radiation and treatment schedule
- Overall health
Short-Term Side Effects of Radiation Therapy:
There are two main types of side effects: acute and chronic. Acute (short-term) side effects occur during the treatment, and typically go away a few weeks after treatment is finished. They may include fatigue, skin reactions, and side effects specific to the area being treated.
Long-Term Side Effects of Radiation Therapy:
Chronic side effects can occur during treatment and last for many months or years after treatment, or they can develop months to years after radiation therapy. They differ according to the area treated and the total dose of radiation therapy received.