Categories
- Bariatric Surgery (11)
- Black Fungus (5)
- Bone Marrow transplant (3)
- Brain Tumor Surgery Navigation Technology (20)
- Cardiac Surgery (66)
- Cardiology (97)
- Computer navigation technology for joint replacements (20)
- Covid Vaccination (17)
- Critical Care (2)
- Dental (19)
- Dermatology (31)
- Dialysis Support Group - “UTSAAH” (11)
- Dietitian (33)
- Emergency Medicine (4)
- Emotional Health (11)
- Endocrinology (33)
- ENT (20)
- Gastroenterology and GI Surgery (53)
- General and Laparoscopic Surgery (21)
- General Surgery (4)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (183)
- Hematology (20)
- Internal Medicine (294)
- Kidney Transplant (50)
- Kidney Transplantation (20)
- Lung Cancer (8)
- Minimal Invasive Surgery (1)
- Mother & Child (20)
- mucormycosis (5)
- Nephrology (61)
- Neurology (147)
- Neurosurgery (68)
- Nutrition and Dietetics (107)
- Omicron Variant (1)
- Oncology (288)
- Ophthalmology (10)
- Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement (86)
- Paediatrics (59)
- Pediatric Nephrology (3)
- Physiotherapy (5)
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery (6)
- Psychiatry and Psychology (90)
- Psychologist (28)
- Pulmonology (72)
- Rheumatology (13)
- Spine Services (21)
- Transradial Angioplasty (16)
- Urology (84)
Query Form
Posted on Apr 19, 2022
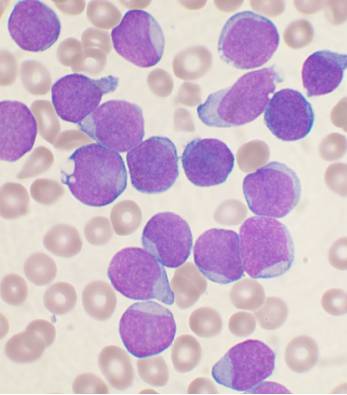
What is Acute Leukemia?
What is Acute Leukemia?
Acute leukemia is a type of blood cancer, that affects thousands of people each year. It can affect individuals of any age, including young children, adolescents, young adults, and senior citizens. The survival of acute leukemia patients has improved over the years. However, many patients still die of this disease.
How common is Acute Leukemia in India?
Acute leukemia is not a very common cancer but the numbers are increasing. As per available data, in India new cases of acute leukemia annually vary from 0.8/100000 to 5/ 100000 population. However, there is under-reporting, and a lot of patients are not diagnosed accurately. So the actual number of patients suffering from acute leukemia may be much more.
What are the symptoms of acute leukemia?
Acute leukemia can present with fever, unusual bleeding manifestations, weakness, lymph node enlargement, aches, and pains. These could be of abrupt onset. Patients usually present with a fever that is not settling with regular medications taken for a reasonable length of time. There is accompanying weakness and easy fatigue in carrying out daily activities. Routine blood tests like complete blood count and peripheral smear pick up some abnormal cells leading to the first suspicion of acute leukemia. There can be bleeding from unusual sites likes gums, heavy menses, irregular menses, bruises in the skin, blood in the stool. There can be enlargement of glands in the neck, armpit or groin area. Some patients complain of bony pains.
What are the tests conducted to diagnose acute leukemia?
As mentioned above, the initial suspicion of acute leukemia can be on the basis of a complete blood count and peripheral smear. This is a simple and low-cost blood test that is easily available even in remote areas and does not require the patient to be fasting. After the initial suspicion, the patient has to undergo further tests to confirm the diagnosis of acute leukemia, to see the type of acute leukemia, and to see the fitness for treatment. A bone marrow test is done in almost all cases to confirm the diagnosis and type of acute leukemia.
What are the types of acute leukemia?
Broadly, acute leukemia can be of two types- acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Acute Myeloid Leukemia is further categorized into multiple types. One unique type of acute myeloid leukemia is acute promyelocytic leukemia. This variety is treated differently and has excellent outcomes.
What are the risk factors for developing acute leukemia?
In most patients, the cause of acute leukemia is unknown. However, it can develop from a pre-existing hematological malignancy like myelodysplastic syndrome [MDS], myelofibrosis, myeloproliferative neoplasms. Patients who have received certain types of chemotherapy drugs or radiotherapy for some other cancer previously in life can also get acute leukemia as a second malignancy. There are some kinds of viral infections and chemical exposures which may predispose to this disease. Some genetic diseases also predispose to acute leukemia. But as stated previously, in most cases the cause is unknown.
What is the treatment for acute leukemia?
Acute leukemia is a medical emergency and its treatment should be started as soon as possible. Delay in starting treatment from the time of diagnosis can be harmful to the patient. Chemotherapy is the mainstay of the treatment of acute leukemia. In recent years some new medicines including targeted therapy have also been introduced in the treatment of acute leukemia. Blood component therapy is also an important component of the treatment of acute leukemia. These patients frequently have anemia and very low platelet counts for which blood components may be required. Patients with acute leukemia are at a very high risk of infections. Hence they may require anti-microbial drugs as prophylaxis or as treatment of infectious diseases. Each patient with acute leukemia is unique and treatment may have to be tailored as per the patient. The age of the patient and various other co-morbidities may play an important role in deciding appropriate treatment for a particular patient. Some patients may require allogeneic bone marrow transplants in addition to chemotherapy.
What are the dietary restrictions for patients with acute leukemia?
Patients with acute leukemia are at a very high risk of infections due to the disease and the effects of chemotherapy. Hence they should take home-cooked food only. Outside food should be avoided. Food should be freshly cooked and eaten while it is warm. The drinking water should preferably be boiled and cooled. Raw vegetables and salads should be avoided. Thick skin fruits eg bananas, watermelons, mangoes, litchis, etc can be consumed provided they are fresh.
Is acute leukemia curable?
Certainly, acute leukemia is curable. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children is one of the most curable cancers. The exact chances of cure for a particular patient depend upon many factors including the disease biology including genetic tests and mutations, the age of the patient, the comorbidities, the fitness for intensive chemotherapy, and the response to initial chemotherapy. These should be discussed in detail with the patient and the treating doctor.
