Diabetes is a condition where your body’s blood glucose levels to rise higher than normal. This also called hyperglycaemia. The body of a person suffering from type 2 diabetes doesn’t use insulin properly and as a result, glucose (sugar) accumulates in the blood. It is a long-term metabolic disorder. The global prevalence of diabetes type 2 was 8.5% in 2014, which means 422 million people, according to WHO and it has only risen since then. In India, there are more than 62 million people suffering from this disorder. The gender related differences in the prevalence of the disease are not much, with it affecting both genders equally.
The symptoms are a direct result of the sugar in your blood. They are:
- Constant hunger
- Constant lack of energy
- Unexplained weight loss
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Itchy skin
- Blurred vision
See a doctor if you experience any of the above mentioned symptoms. Always trust premier medical institutions like Paras Hospitals which have specialized departments for expert care of your condition.
The cause of type 2 diabetes is the pancreas producing little insulin which is not enough. Another leading cause could be the body developing insulin resistance. Doctors and researchers however, don’t know what causes some people to develop diabetes, and others to not, but there are number of risk factors that increase the risk:
- Excess Weight: It is a primary risk factor for type 2 diabetes. The more fatty tissue one has, the more chances of their developing resistance to insulin.
- Accumulation of fat in abdomen: If your body stores fat primarily in your abdomen, it increases the chances of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Inactivity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle, devoid of activity is another great risk factor, as the glucose in your body is not used up, decreasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin.
- Family History: The leading risk factor in diabetes type 2 is if someone in your family has or has had it.
- Age: The chances of getting diabetes increase as one gets older, especially after 45.
- Prediabetes: This is a condition when your body sugar level is higher than normal, although not high enough to be classified as diabetes. But if untreated, prediabetes turns into full-fledged diabetes type 2.
Diabetes is a life-long disease which has to be managed. The main goal here is to keep the blood sugar levels as normal as possible. To do that, one has to manage a few things, like:
- Healthy Eating
- Regular Exercise
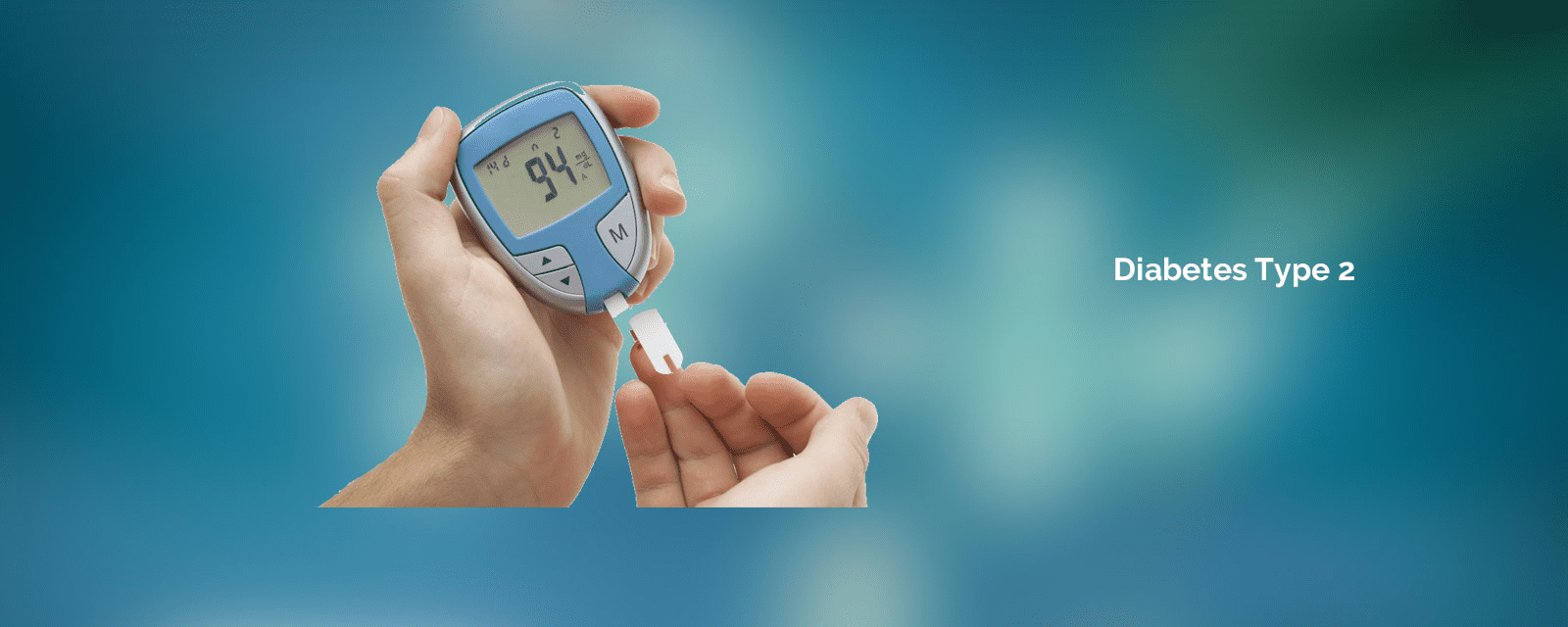
- Monitoring Blood Sugar regularly and timely
- Possibly, if your doctor prescribes it, diabetes medication or insulin therapy
The medications either improve body’s sensitivity to insulin, or help the pancreas secrete more insulin. If these don’t work, or if your doctor prescribes it as the first choice, one shot of insulin is injected at night daily (yourself), which is known as insulin therapy. Healthy eating and regular exercise are imperative, and sometimes are enough to decrease blood sugar to a near-normal level.


 Call us at
Call us at