Categories
- Bariatric Surgery (11)
- Black Fungus (5)
- Bone Marrow transplant (3)
- Brain Tumor Surgery Navigation Technology (20)
- Cardiac Surgery (66)
- Cardiology (97)
- Computer navigation technology for joint replacements (20)
- Covid Vaccination (17)
- Critical Care (2)
- Dental (19)
- Dermatology (31)
- Dialysis Support Group - “UTSAAH” (11)
- Dietitian (33)
- Emergency Medicine (4)
- Emotional Health (11)
- Endocrinology (33)
- ENT (20)
- Gastroenterology and GI Surgery (53)
- General and Laparoscopic Surgery (21)
- General Surgery (4)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (183)
- Hematology (20)
- Internal Medicine (294)
- Kidney Transplant (50)
- Kidney Transplantation (20)
- Lung Cancer (8)
- Minimal Invasive Surgery (1)
- Mother & Child (20)
- mucormycosis (5)
- Nephrology (61)
- Neurology (147)
- Neurosurgery (68)
- Nutrition and Dietetics (107)
- Omicron Variant (1)
- Oncology (288)
- Ophthalmology (10)
- Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement (86)
- Paediatrics (59)
- Pediatric Nephrology (3)
- Physiotherapy (5)
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery (6)
- Psychiatry and Psychology (90)
- Psychologist (28)
- Pulmonology (72)
- Rheumatology (13)
- Spine Services (21)
- Transradial Angioplasty (16)
- Urology (84)
Query Form
Posted on Apr 19, 2022
Chronic Kidney Disease – An Overview
Chronic kidney Disease (CKD) is a growing health concern in society. It is estimated that about 11 to 13% of the adult population in the world suffers from CKD and the numbers are expected to rise in future. In India, more than one lakh new patients develop CKD every year.
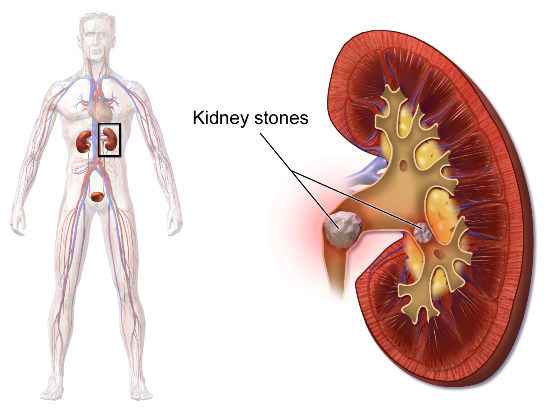
Diabetes mellitus is the most common cause of CKD accounting for about 30% to 40% of adult cases. Conversely, 20 to 30% of diabetics will develop diabetic nephropathy and CKD during their life. Therefore as the number of diabetic patients increases, the incidence of CKD is expected to follow. Other common causes of this disease include Hypertension, ChronicGlomerulonephritis, certain hereditary diseases ( ex. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease), renal stone disease, prolonged use of pain killer medicines and recurrent UrinaryTract Infection especially in children because of anatomical abnormalities of urinary tract.
Early detection is important to prevent the progression of CKD. The National Kidney Foundation (a U.S based major voluntary health organization) recommends all patients of diabetes, hypertension and healthy people with a family history of kidney disease or age more than 65 years should be screened for the presence of CKD. Similarly those with symptoms suggestive of kidney disease should also be evaluated for the same. Early symptoms of the disease include tiredness, less energy, poor appetite, swelling of feet and ankles, puffiness around the eyes (especially in mornings), need to urinate more often (especially at night) and a dry itch skin.
Diagnosis and timely proper treatment are important. Primary medical treatment includes diuretics, meticulous control of blood pressure, blood sugar, lipids and management of anemia, bone disease and pruritus (itching).It is also important to maintain ideal body weight, do regular exercise and avoid smoking and alcohol. Regular long term use of pain killers should be avoided as they are notoriously nephrotoxic.
One important point to note is that cardiovascular disease is much more common in CKD patients than in the normal population and prevention and timely treatment of the same are extremely important.
Patients with advanced kidney disease needs to be on dialysis. Dialysis is a procedure that is a substitute for many of the normal functions of the kidneys. Hemodialysis is a form of dialysis where the blood in the body is continuously removed and passed through an artificial kidney (Dialysis machine) which cleans it and the purified blood is returned back into the body. This form of dialysis needs to be done at least twice a week with each session lasting four hours. It is a lifelong requirement unless the patient undergoes a renal transplant. Alternative form of such maintenance dialysis is peritoneal dialysis which includes CAPD (Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis) and APD (Automated Peritoneal Dialysis)
Renal Transplant is a good option for patients with advanced CKD. It should especially be considered in younger patients and also in the not very elderly (those less than 65 years). It provides a good quality of life to such patients and prevents the need for regular dialysis.